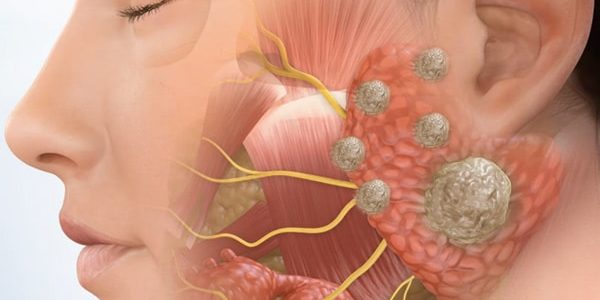
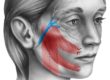
Salivary gland tumors are tumors originating from the salivary glands. These tumors can be benign or malignant. Saliva helps digestion with the enzymes it contains. It also contains substances called antibodies that protect the body against oral and throat infections.
The largest salivary gland is called the parotid gland. It is located right in front of the ears. Most salivary gland tumors occur in this gland. Most parotid gland tumors are benign, ie they are not cancerous. However, most malignant salivary gland tumors are also seen in this gland.
Submandibular glands are found under the chin, they are smaller and discharge the saliva secretion under the tongue. Approximately half of the tumors originating from this gland are malignant, ie cancer.
The smallest salivary gland is the sublingual gland. Located under the base of the mouth. Tumors originating from these glands are very rare.
What are the risk factors for salivary gland tumors?
The risk factors for salivary gland tumors are;
Aging
Male sex
Exposure to radiation
Exposure to radioactive substances
Family history
Tobacco use
Alcohol consumption
Dietary habits
Cell phone usage
What are the symptoms of salivary gland tumors?
Swelling in mouth, cheek, jaw or neck, mass, lump
Pain in mouth, cheek, chin, ear or neck
Numbness on part of face
Muscle weakness on one side of the face
Problem opening the mouth fully
Pouring liquid from an ear
Swallowing difficulty
What is the Treatment of Salivary Gland Tumors?
Treatment of salivary gland tumor is removal of salivary gland by surgery. During surgery, some or all of the cancer tissue and the surrounding salivary gland are removed. Sometimes the tissues around the salivary gland can also be removed. The aim is not to leave any cancer cells on the outer edges of the removed tumor. If the cancer is high-grade or spread to the lymph nodes, the lymph nodes on the same side of the neck are also removed.