What is goiter?
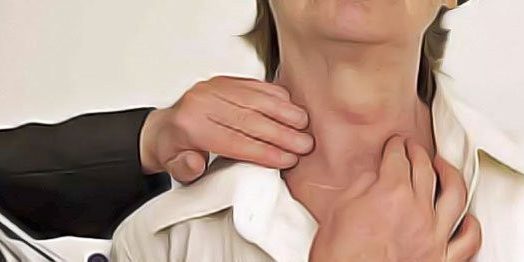
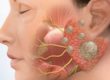
Goitre is a condition where the thyroid gland grows. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located just in front of the neck. Thyroid hormones are secreted from the thyroid gland. These hormones have a very important effect on the metabolism and brain especially in the body.
Why Does Thyroid Gland Grow?
The most common cause of thyroid gland growth is the lack of iodine. Iodine is a substance necessary for the production of thyroid hormones. In the absence of iodine, not enough thyroid hormones can be made. In this case, another hormone (TSH) produced in the brain stimulates the thyroid gland to continuously produce hormones. This stimulation results in growth of the thyroid gland.
Another common cause of growth in the thyroid gland is the so-called Hashimoto thyroid. In this disease, the thyroid gland is considered foreign by the immune system and is attacked. The thyroid gland that is destroyed by these attacks cannot produce enough hormones. In this case, the brain begins to constantly stimulate the thyroid gland to produce hormones, resulting in growth of the thyroid gland. Again in Graves’ disease, the immune system causes thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin secretion. This causes growth in the thyroid gland. HCG hormone secreted from the placenta during pregnancy causes growth in the thyroid gland.
What are Goiter Symptoms?
The disease does not cause any symptoms in some people. In some people, neck swelling, difficulty swallowing, cough, shortness of breath and sore throat may be seen. In addition, goiter in the thyroid gland may produce some thyroid hormone for months or a few symptoms. Fatty, constant drowsiness, weakness, drowsiness, dryness and coarsening of the skin, constipation and hair loss may occur due to insufficient hormone secretion. Diarrhea, heart palpitations, headache, increased appetite, tremor, irritability and nausea may occur due to excessive hormone secretion.
How is goiter treatment?
Treatment options for goiter treatment include drug therapy, radioactive iodine therapy and surgery. One or more of these methods may be applied together. If the patient has hormone deficiency, the missing hormone is replaced. If there is a surplus of hormones, drugs that suppress this thyroid hormone or radioactive iodine are used. Particularly in the surgical treatment of nodular goiter, some or all of the thyroid gland is removed. Some undesirable conditions may occur during goiter surgery. Hoarseness, calcium deficiency due to accidental removal of parathyroid glands are some of them.