What is Otosclerosis?
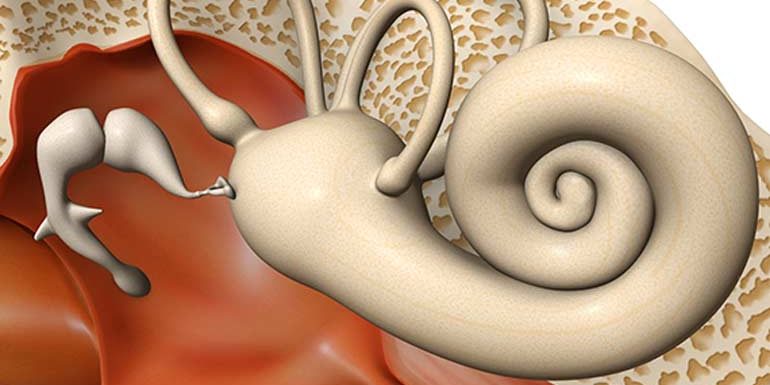
Ear calcification, or otosclerosis as its medical name, is a disease caused by a disorder related to bone formation and destruction in the bones of the middle ear which is the closest bone to the inner ear. Calcification in the stirrup bone prevents ossification in the middle ear. When the bones cannot vibrate, the sound cannot be transmitted to the inner ear.
What are the Symptoms of Otosclerosis?
Symptoms of otosclerosis ie ear calcification occur late. The onset of the disease is silent, so it is difficult to notice and progresses. The most important symptom of otosclerosis is hearing loss and tinnitus. Hearing loss can be in one or both ears. Hearing loss progresses gradually. Dizziness and balance problems may also accompany these symptoms.
What are the causes of ear calcification?
The cause of otosclerosis is not clear. There is inherited susceptibility to the disease. The disease usually begins in the twenties. It is more common in women.
What is Otosclerosis Treatment?
Methods used in the treatment of otosclerosis; observation, use of hearing aids, sodium fluoride treatment and surgical treatment. Patients with mild hearing loss can be monitored and monitored regularly. Depending on the course of the disease, another treatment option may be decided.
Sodium fluoride treatment can be used if the disease has reached the inner ear, has dizziness and imbalance problems, and the disease focus has not yet ossified.
The use of hearing aids is not recommended in patients who are eligible for surgery. Otosclerosis surgery is called stapedectomy or stapedotomy. In operation, calcareous stirrup is partially or completely removed and replaced with a prosthesis. This procedure can be performed under local or general anesthesia according to the preference of the surgeon performing the surgery.